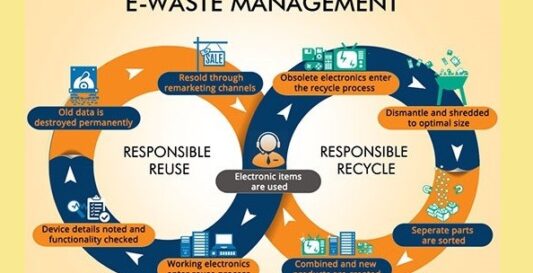
E-waste recycling refers to the process of collecting, dismantling, sorting, and processing electronic waste (e-waste) to recover valuable materials and components for reuse or recycling. The goal of e-waste recycling is to divert electronic waste from landfills and incinerators, reduce environmental pollution, conserve natural resources, and minimize the energy and carbon footprint associated with the production of new electronic products.
The e-waste recycling process typically involves several key steps:
- Collection: E-waste is collected from consumers, businesses, and other sources through various channels, including drop-off locations, recycling centers, manufacturer take-back programs, and electronic waste recycling events.
- Sorting and Dismantling: Once collected, e-waste is sorted into different categories based on the type of electronic device and its components. Devices are then dismantled to separate reusable and recyclable materials from non-recyclable components and hazardous substances.
- Material Recovery: Reusable and recyclable materials such as metals (e.g., copper, aluminum, gold, silver), plastics, glass, and other valuable components are recovered from e-waste through mechanical shredding, crushing, grinding, and separation processes.
- Processing: Recovered materials are processed and prepared for reuse or recycling. Metals are melted down and purified for reuse in the manufacturing of new electronic products or other applications. Plastics are cleaned, shredded, and pelletized for use in the production of new plastic products.
- Hazardous Waste Management: Hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and brominated flame retardants are properly managed and disposed of in accordance with environmental regulations to prevent environmental contamination and protect human health.
- Data Destruction: Before recycling, electronic devices containing sensitive or personal data are securely wiped or destroyed to protect privacy and prevent data breaches.
- End-of-Life Management: Any remaining non-recyclable or hazardous components are disposed of safely and responsibly, following applicable regulations and guidelines for waste disposal.
E-waste recycling helps to conserve natural resources, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and minimize the environmental and health risks associated with improper e-waste disposal. It also contributes to the circular economy by recovering valuable materials from electronic products and reintroducing them into the manufacturing process, thereby reducing the need for virgin materials and reducing waste generation.