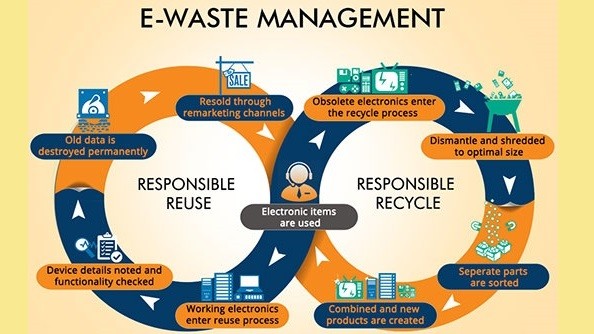
As we navigate the digital age, the proper management of electronic waste (e-waste) has become increasingly crucial. E-waste, consisting of discarded electronic devices, poses significant environmental and health hazards if not managed responsibly. To address this challenge, it is imperative that we prioritize e-waste management at both individual and organizational levels. By embracing practices such as recycling, refurbishment, and responsible disposal, we can mitigate the environmental impact of e-waste and contribute to a more sustainable future.
E-waste management encompasses a comprehensive approach to handling electronic waste, aiming to minimize its environmental impact while maximizing resource recovery and promoting sustainable practices. This multifaceted process involves various stages, including collection, sorting, dismantling, recycling, and proper disposal of electronic devices. Through effective e-waste management, obsolete or end-of-life electronics are diverted from landfills and incinerators, reducing the release of hazardous substances into the environment and mitigating potential health risks. By implementing responsible recycling practices, valuable materials such as metals, plastics, and other components are recovered and reintegrated into the manufacturing supply chain, conserving natural resources and reducing the carbon footprint associated with the production of new electronic products. Additionally, e-waste management involves raising awareness among consumers, businesses, and policymakers about the importance of responsible consumption, recycling, and disposal of electronic devices to create a sustainable and circular economy for electronics.
Effective e-waste management involves several key steps. Firstly, it requires the establishment of convenient and accessible e-waste collection points, where individuals and businesses can dispose of their unwanted electronics. These collection points should be equipped to handle various types of e-waste and ensure that materials are properly sorted and processed for recycling or disposal. Additionally, it is essential to raise awareness about the importance of e-waste management through education and outreach initiatives. By educating the public about the environmental and health risks associated with e-waste, we can encourage responsible consumption and disposal practices.
Furthermore, collaboration among governments, businesses, and communities is essential for implementing effective e-waste management strategies. Policymakers can play a critical role by enacting regulations and incentives to promote e-waste recycling and proper disposal. Similarly, businesses should take responsibility for the lifecycle of their products, from design to end-of-life management, by prioritizing recyclability and incorporating sustainable practices into their operations. Finally, individuals can contribute to e-waste management efforts by reducing their electronic consumption, extending the lifespan of their devices through repair and reuse, and recycling old electronics whenever possible.
In conclusion, e-waste management is a collective responsibility that requires cooperation and commitment from all stakeholders. By adopting sustainable practices and working together to address the challenges of e-waste, we can protect the environment, conserve resources, and create a healthier planet for future generations.