Introduction:
Solid waste management is a critical aspect of environmental sustainability and public health. With increasing urbanization and industrialization, the generation of solid waste has surged, necessitating robust strategies for its effective management. This note outlines a comprehensive approach to solid waste management aimed at mitigating environmental pollution, promoting resource recovery, and fostering community engagement.
Key Components:
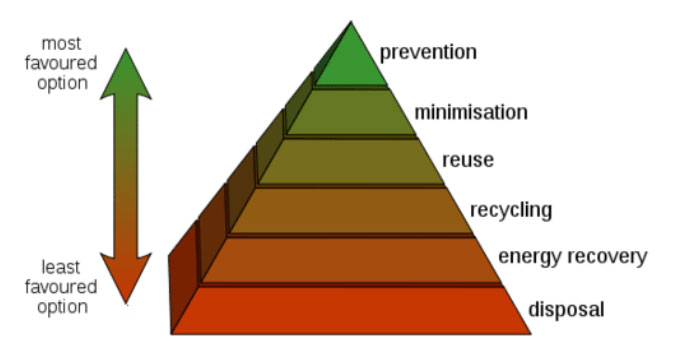
1. Waste Minimization:
– Emphasize the importance of waste reduction at the source through awareness campaigns, education programs, and incentivized practices such as composting, recycling, and reusing.
– Implement policies and regulations to encourage manufacturers and consumers to adopt eco-friendly packaging and products, thus minimizing waste generation.
2. Segregation and Collection:
– Establish efficient waste segregation at the household, commercial, and industrial levels to facilitate proper disposal and recycling.
– Deploy segregated collection systems with designated bins for recyclables, organic waste, and non-recyclables.
– Ensure regular collection schedules and invest in adequate infrastructure and manpower for prompt waste removal.
3. Recycling and Resource Recovery:
– Develop recycling facilities and promote the establishment of material recovery facilities (MRFs) for sorting and processing recyclable materials.
– Encourage public and private partnerships for investment in recycling infrastructure and technologies.
– Support initiatives for converting organic waste into compost or energy through anaerobic digestion or other sustainable methods.
4. Treatment and Disposal:
– Invest in modern waste treatment facilities such as waste-to-energy plants, sanitary landfills, and incineration facilities with stringent emission controls.
– Prioritize environmentally sound disposal methods to minimize pollution and safeguard public health.
– Implement strict regulations and monitoring mechanisms to ensure compliance with waste disposal standards.
5. Public Awareness and Participation:
– Launch educational campaigns to raise awareness about the importance of proper waste management practices and their impact on the environment.
– Foster community participation through citizen engagement programs, volunteer clean-up drives, and involvement in waste management initiatives.
– Encourage the adoption of sustainable lifestyles and responsible consumption habits among individuals and communities.
Conclusion:
A holistic approach to solid waste management is essential for addressing the challenges posed by escalating waste generation. By implementing strategies focused on waste minimization, segregation, recycling, treatment, and community involvement, we can achieve significant progress towards a cleaner environment, resource conservation, and sustainable development. Collaboration among government agencies, private sector stakeholders, and the public is paramount in realizing the vision of effective solid waste management for present and future generations.