Electronic waste (e-waste), is a generic term used to describe all types of old, end-of-life or discarded electrical and electronic equipment, such as household appliances; office information and communications equipment; entertainment and consumer electronic equipment; lighting equipment; electric and electronic tools; toys; and leisure, sports and recreational equipment that are powered by electricity. E-waste contains Continue Reading
Lack of water, sanitation and hygiene results in the loss of 400,000 lives per year in India. 600 million people - nearly half India’s population - face acute water shortage, with close to 200,000 dying each year from polluted water. Nearly 70 per cent of India’s water is contaminated, impacting three in four Indians and Continue Reading
Scientific studies and planning: It means understanding the type of waste, the costs involved, and the best locations for disposal facilities. India needs to invest in innovative technologies and develop a better recycling infrastructure. Improve waste collection: India has more frequent services, use machines to collect waste, and coordinates the timing of collection with waste generation. Combining informal and Continue Reading
India faces challenges in managing waste. The informal sector plays a significant role in extracting value from waste, but many challenges remain. Rapid urbanization: Urban areas with 377 million people generate about 62 million tons of solid waste every year. However, only 43 million tons are collected, and the rest ends up untreated or in landfills. Continue Reading
We can classify solid waste in a number of ways. Based on the effects of solid waste on the environment and the health of humans, it can be differentiated between hazardous waste and non-hazardous waste. Hazardous Waste Wastes generated in industries and hospitals are generally hazardous in nature as they contain toxic substances. Resource Conservation Continue Reading
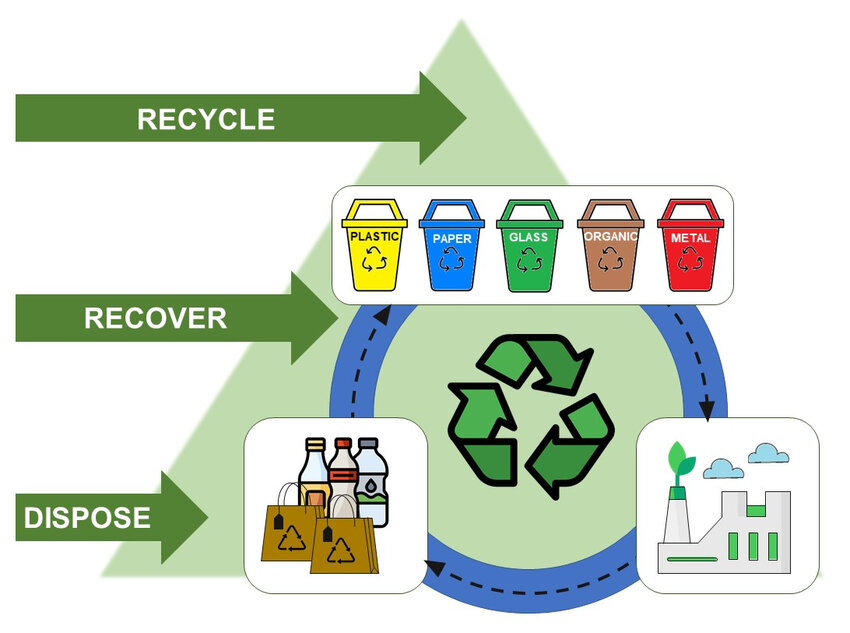
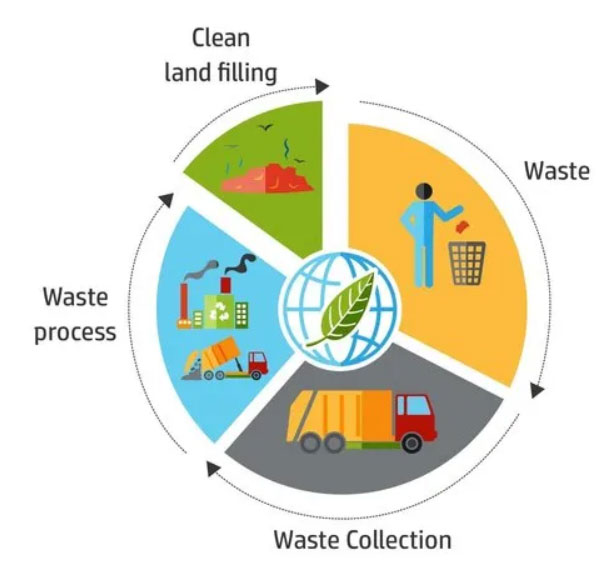
The term "Solid Waste Management" refers to the collection, treatment, and disposal procedure for solid wastes. Wastes are gathered from various sources and are disposed of through the waste management process, which involves the collection, transportation, treatment, analysis, and disposal. Solid waste is a non-liquid, non-soluble material ranging from municipal garbage to industrial waste that Continue Reading
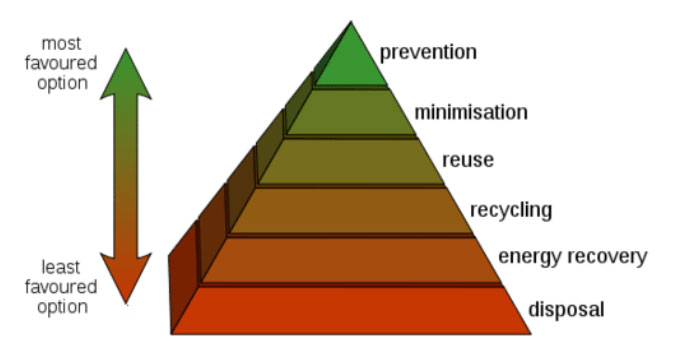
Introduction: Solid waste management is a critical aspect of environmental sustainability and public health. With increasing urbanization and industrialization, the generation of solid waste has surged, necessitating robust strategies for its effective management. This note outlines a comprehensive approach to solid waste management aimed at mitigating environmental pollution, promoting resource recovery, and fostering community engagement. Continue Reading